Charles Amirkhanian with the composers of OM 21
Much needed rain pummeled the city by the bay on all three days of OM 21 dampening, perhaps, some attendance but not the enthusiasm of the audience or the performers. In most ways this concert was a continuation of the celebration begun last year commemorating 20 years of this festival. Returning this year were Gavin Bryars (OM7) and Meredith Monk (OM1).
Until last year no composer had appeared more than once at this series. For those unfamiliar with OM it is worth noting that the process has been for the 8-10 selected composers spend a week at the Djerassi Arts Center in Woodside, California sharing and discussing their work before coming to San Francisco for performances of their work.
As it turns out this year’s concert series will be the last to follow that format. Apparently OM has become the victim of gentrification and has had to move out of its Valencia Street offices and will now opt for various concerts throughout the year as they have done but without the big three-day annual festival and the residency at Djerassi.
The archives of OM are now going to be housed at the University of California Santa Cruz where they will reside along with the Grateful Dead archives. I do believe that Mr. Amirkhanian lived near Phil Lesh of the Grateful Dead when he lived in San Francisco some years ago so it seems fitting that these two archives will peacefully coexist in that space (also coming to UCSC will be OM 21 composer Larry Polansky though not in an archive).
This is certainly a change but this is a festival which has endured various changes in time and venue led throughout by the steady hand of the Bill Graham of contemporary music concerts, Charles Amirkhanian (both men have had a huge impact on music in the bay area as well as elsewhere and it is worth noting that the Contemporary Jewish Museum will have a tribute to Graham this year).
Actually Other Minds traces its provenance to the Telluride, Colorado Composer to Composer festival (also led by Amirkhanian) and later morphed into OM with the leadership of president (now emeritus) Jim Newman back in the early 1990s. There is a short excellent film describing OM’s history on Vimeo here.
It is the end of a chapter but, as Amirkhanian explained, there are many exciting concerts coming up which will keep Other Minds in the earshot of the astute contemporary music aficionados on the west coast. Next year, for example, will include several very exciting concerts celebrating the 100th birthday anniversary of beloved bay area composer Lou Harrison.
My apologies for the delay in posting which was due to both the richness of the experience and the exigencies of my day job and other responsibilities. I hope that readers will find this post to have been worth the wait.

Nordic Voices
Starting our rainy day were the extremely talented singers known as Nordic Voices. Lasse Thoresen‘s Solbøn ( Sun Prayer) (2012) and Himmelske Fader (Heavenly Father) (2012) both required keen listening and required the use of extended vocal techniques such as multiphonics. The singing appeared effortless and even fun for the ensemble but that speaks more to their expertise and preparedness than any ease in terms of the score.
It is always difficult to judge a composer’s work by only a small selection from their output but Thoresen’s virtuosity and subtle use of vocal effects suggests a highly developed artist and it would seem worth one’s time to explore more of this gentleman’s oeuvre.

Lasse Thoresen takes the stage to acknowledge the applause.
Next was an unusual, humorous/dramatic work by Cecile Ore called Dead Pope on Trial (2015/16) with a libretto by Bibbi Moslet. This Other Minds commission was given its world premiere at this concert. The work is based on the story of a medieval pope who was taken from his grave no fewer than six times for various perceived offenses. It is a mix of irony and humor in a sort of madrigal context. The work was in English and had the nature of a conversation between the singers. No doubt a challenging piece, it was sung very well and the composer seemed as pleased with the performance as much as the audience.

Cecile Ore smiling as she acknowledges the applause for the wonderful premiere performance of her new work, Dead Pope on Trial.
As if in a demonstration of sheer stamina in addition to virtuosity Nordic Voices took the stage again, this time for some Madrigals (2002/2016) by returning artist Gavin Bryars. Bryars is no stranger to Other Minds or to madrigals and such older musical forms from the renaissance and before. He has extensively explored vocal writing and medieval harmonies in many previous works. Though categorized as being a “minimalist”, Bryars actually has produced a huge range of music in all forms including opera, chamber and orchestral music.
His madrigals have been written for the Hilliard Ensemble and each book is distinguished by the madrigals having been written on a specific day of the week. The first book on Mondays, etc. They are settings of Petrach’s sonnets and are sung in the original Italian of his day. On this night we were treated to four madrigals from Book Two and the premiere of a madrigal from Book Four. That madrigal was dedicated to Benjamin Amirkhanian, the father of Charles Amirkhanian who celebrates his 101st birthday this summer.
I had the opportunity to meet and speak briefly with the affable Mr. Bryars. His generous spirit pervaded our conversation and he spoke very highly of both his visits to Other Minds. If you don’t know this man’s music you are doing yourself a great disservice.

A very pleased Gavin Bryars deflects the applause and adulation to the amazing Nordic Voices for their astounding performance of five of his madrigals.
The singers of Nordic Voices sustained a high level of virtuosity as well as sheer stamina as they sang for nearly two hours in the opening pieces of this concert series. No time was lost setting the stage for the performance of the next piece, another premiere, Algebra of Need (2016) for electronic sampling and string quartet by Bang on a Can member Phil Kline.

FLUX Quartet playing at SF Jazz, 2016
The Flux Quartet was featured in the next two (and last) works on this long program. Algebra of Need is Kline’s meditation on the words and the cadences of the iconic writing and voice of the late William S. Burroughs (gone 19 years as of this writing). The familiar voice seemed to go in and out of clearly audible, at times mixed more closely with the string writing in this intense homage.

A satisfied looking Phil Kline leans in to embrace the first violin of the Flux Quartet after their premiere of his Algebra of Need.
The Bang on a Can collective was also represented tonight by Michael Gordon. The Sad Park (2008) for string quartet and electronics put a most decidedly disturbing conclusion on the evening. This piece, which samples the voices of children (one of them Gordon’s) as they spoke of their experience of the 9/11 Twin Towers attacks.
The effect was, as no doubt intended, harrowing leaving a pretty strange and unsettling feeling as we walked away from the concert into the still rainy night.

Michael Gordon embraces the FLUX Quartet’s first violin after a stunning performance of The Sad Park.
The rain continued on Saturday but the crowd was noticeably larger for the second night which opened with the usual panel discussion.

left to right: Meredith Monk, John Oswald, Nicole Lizee, Eliot Simpson, Larry Polansky, Oliver Lake and Charles Amirkhanian in a panel discussion prior to the concert
This evening began with a performance by the wonderful bay area violinist Kate Stenberg of a piece which was a sort of antidote to the somber, The Sad Park from the previous night. Again the composer was Michael Gordon and the piece was Light is Calling (2004), a collaboration with filmmaker Bill Morrison. Though hardly a happy piece Light is Calling is perhaps elegiac and the composer seems to achieve some of his stated intent to find some healing in the wake of a disaster to which he was all too close.
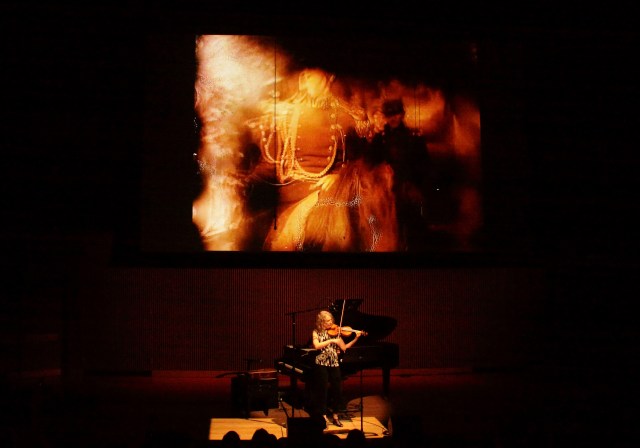
Kate Stenberg plays violin beneath the projection of a Bill Morrison film in Michael Gordon’s, Light is Calling
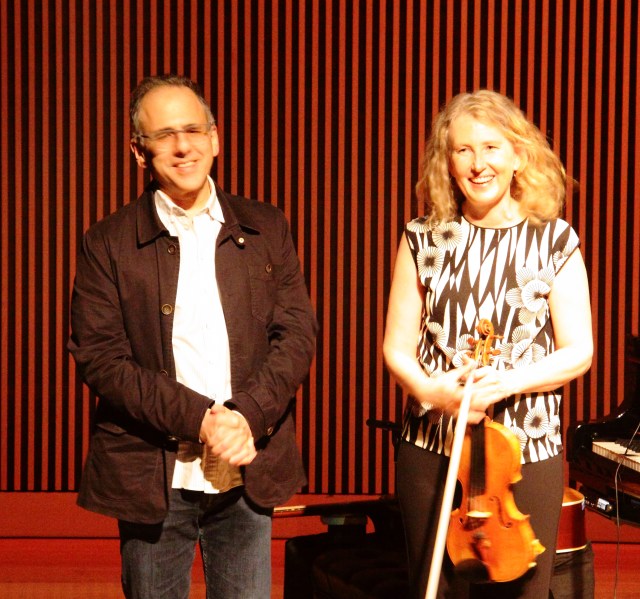

Michael Gordon and Kate Stenberg accepting the applause of an appreciative audience.
Next up was John Oswald, a Canadian composer whose career took off in infamy when his Plunderphonic CD, released to radio stations in the early 1980s, became the subject of legal battles over the meaning of copyright law in light of digital sampling. Fortunately Oswald won the right to publish his work and his Plundrphonics concepts now underlie much of his compositional process. Until this night I had not heard any but his Plunderphonic CDs so the introduction to his live music was a revelation.
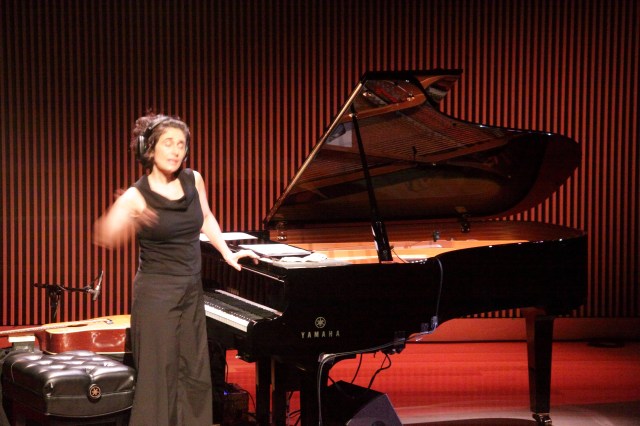

Pianist and (at least here) multi-instrumentalist Eve Egoyan performing with a Yamaha Disklavier and other instruments.
The first piece she did was called Homonymy (1998/2015) was originally written for chamber orchestra and was then transcribed for Egoyan and her prepared disklavier et al. It is a piece based on linguistic elements and with a visual component as well.

Eve Egoyan performing Homonymy with overhead projections.
Nicole Lizee’s David Lynch Etudes (2015) was the next piece and also made use of the projection screen. The subtitle of the piece indicates it is for “disklavier and glitch”. Well life imitated art as some sort of glitch prevented the projection from functioning at first but this was rather quickly resolved and we were treated to excerpts of scenes from several David Lynch films with the piano playing some of the rhythms of the dialog in an exchange that puts this writer in the mind of music like Scott Johnson’s “John Somebody” and Steve Reich’s incorporation of speech rhythms in works like, “The Cave”.
Nicole Lizee is a Canadian composer and was the youngest composer on this year’s program.

Eve Egoyan playing Nicole Lizee’s David Lynch Etudes with projected scenes/glitches from Lynch’s films.
The work is one of a series of pieces inspired by films and was executed with apparent ease by pianist Eve Egoyan who played the disklavier (both the keyboard and directly on the strings), a guitar and perhaps other gadgets . The piece kept her quite busy and the associations I described above sound nothing like this work actually. These etudes were a unique, typically Other Minds sort of experience, one that expands the definition of musical composition.

Nicole Lizee (l) with Eve Egoyan absorbing the audience’s appreciation of the David Lynch Etudes.
Two more John Oswald compositions graced the program next. Palimpia (2016) is a six movement piece for disklavier with pianist playing as well. Oswald says it is actually his first composition for piano.

John Oswald embracing pianist Egoyan and enjoying the audience applause for his work.
Well I did say there were two more Oswald pieces but this last one was a masterful plunder by this truly unusual composer. Here Oswald conjured the playing as well as the image of the late great Glenn Gould who was seen actually playing Invaria (1999) with the disklavier performing along with the film of Gould performing this music. It was, for this writer, a spellbinding experience. He has raised the dead in the name of music. Wow! It was an amazing and heartfelt homage to a fellow great Canadian musician.

Glenn Gould playing John Oswald
Larry Polansky (1954- ) is well known as a teacher and as a composer but one is hard pressed to find much in the conventional discography of his work. The few discs out of his amazing electronic music (and one disc of piano variations) represent only a small fraction of his output and represent only one genre of music which he has mastered. However the astute listener needs to be advised to look online to look, listen and hear some of the bounty of his creative output. Check out the following sites: Frog Peak Music (Polansky’s publishing site which includes music and scores by a great many interesting composer in addition to himself and Dartmouth Page (which contains link to various recordings, writings, computer software, etc.

Giacomo Fiore (left) and Larry Polansky playing Polansky’s ii-v-i (1997)
As an amateur musician who has enough trouble simply tuning a guitar it made my knees weak to watch these musicians effortlessly retune as they played. Polansky’s experimentation with alternate tunings is an essential part of many of his compositions.

Fiore and Polansky changing their tunings mid-phrase in a stunning demonstration of virtuosity with pitch changes.
The program then moved from the electric to the acoustic realm with Polansky’s folk song arrangements. Eliot Simpson, the pedagogical progeny of the great David Tanenbaum (who played these concerts last year at OM 20), played the just intonation National Steel Guitar and sang.
Let me say just two things here. First, these are not arrangements like Copland’s Old American Songs and second, I will never hear these folk songs quite the same way again. Polansky’s interest in folk music and Hebrew cantillation along with alternate tunings produces what the ears hear as perhaps a different focus. In these pieces he did not stray too far from the original (as he does in his Cantillation Studies) but one is left with distinctly different ways of hearing and thinking about this music and the listener is left richer for that. It is a journey worth taking and Simpson played with both passion and command.

Eliot Simpson playing a selection of Larry Plansky’s Songs and Toods
Polansky returned to the stage for a performance of his 34 Chords (Christian Wolff in Hanover and Royalton) (1995). Again we were treated to the virtuosic use of alternate tunings performed live (and again with live re-tunings) by the composer.

Oliver Lake delivering a blistering free jazz improvisation.
Continuing with the solo performer theme we were privileged to hear the virtuosic jams of Oliver Lake (1942- ) whose long career is legendary in the jazz world. The “mostly improvised” (according to the composer) Stick was played on two different saxophones in what appeared to be as intense an experience for the performer as it was for the audience.

Oliver Lake takes a final bow at the end of the second concert of OM 21
The emotional workout was received warmly by the audience.

Charles Amirkhanian introduces Meredith Monk on the final day of OM 21
There was no panel discussion on the third day of OM 21. This matinée was dedicated entirely to the work of Meredith Monk (1942) who, fittingly was one of the featured artists in the first Other Minds gathering in 1993. Now a recipient of the National Medal of the Arts this beloved artist returns to OM 21. Though the rain continued the house appeared to be full.

Meredith Monk playing a Jaw Harp and singing in one of her early solo songs.
Monk played a selection of material from various periods in her career in a mostly chronological survey which she called The Soul’s Messenger. She began with selections from her solo songs and proceeded to her voice and piano music, then to her work with multiple voices and instruments.

Meredith Monk performing her signature Gotham Lullaby
Most of the audience seemed to have a comfortable familiarity with the individual works she offered on this night which effectively gave a picture of her career. Monk was in good voice and appeared to enjoy her performance.

Long time collaborator Katie Geissinger and Allson Sniffin joined in the next selection
The stage was set to allow for the dance/movement that is an essential part of Monk’s works. She originally trained as a dancer.

Monk and long time collaborator Katie Geissinger reacting to the appreciative audience
In addition to the grand piano the stage was set with two electronic keyboards, an essential sound in many of Monk’s works.

Monk at one of the electronic keyboards
Woodwind player Bodhan Hilash joined the ensemble for the last set of pieces.

From left: Bodhan Hilash, Meredith Monk, Allison Sniffin and Katie Geissinger
The audience gave a standing ovation at the end resulting in 3 curtain calls.

Left to right Allison Sniffin, Meredith Monk, Katie Geissinger and Bodhan Hilash receiving a standing ovation.
And the properly prepared artist came back for an encore of her song Details.

Meredith Monk performing an encore at the final concert of OM 21
It was a fitting finale to a great OM 21, fitting to have this artist who appeared on the first iteration of Other Minds returning now crowned with a National Medal of the Arts and clearly beloved by the audience. Her music like her lovely smile fade to the edge of memory like that of the Cheshire Cat on a truly triumphant finale.
And, despite some format changes, who knows what treasures continue to lie in store? I will be watching/listening and so, apparently will many others. Keep an eye on www.otherminds.org . I know I will.








































































































